/
3D Views - Planes and Relief Surfaces
3D Views - Planes and Relief Surfaces
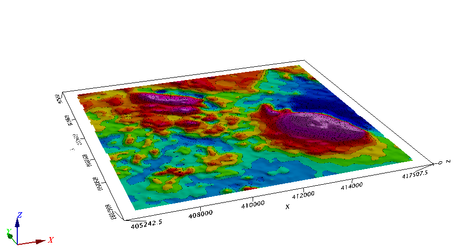
Draw to a Flat Plane in 3D
In this first lesson we will simply draw to the default drawing plane on a new 3D view.
tmo_on_3d_plane.py
import geosoft.gxpy.gx as gx
import geosoft.gxpy.view as gxview
import geosoft.gxpy.group as gxgroup
import geosoft.gxpy.agg as gxagg
import geosoft.gxpy.grid as gxgrd
import geosoft.gxpy.viewer as gxviewer
gxc = gx.GXpy()
grid_file = 'Wittichica Creek Residual Total Field.grd'
# create a 3D view
with gxview.View_3d.new("TMI on a plane",
area_2d=gxgrd.Grid(grid_file).extent_2d(),
coordinate_system=gxgrd.Grid(grid_file).coordinate_system,
overwrite=True) as v:
v3d_name = v.file_name
# add the grid image to the view, with shading, ands contour
gxgroup.Aggregate_group.new(v, gxagg.Aggregate_image.new(grid_file, shade=True, contour=20))
gxgroup.contour(v, 'TMI_contour', grid_file)
# display the map in a Geosoft viewer
gxviewer.view_document(v3d_name, wait_for_close=False)
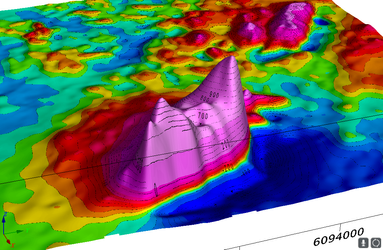
Draw on a 3D Relief Surface
In this lesson we use the data values to define a 3D relief surface for the drawing plane, which transforms from a flat plane to a function surface with function relief defined by the grid data values.
tmi_as_3d_relief.py
import geosoft.gxpy.gx as gx
import geosoft.gxpy.view as gxview
import geosoft.gxpy.group as gxgroup
import geosoft.gxpy.agg as gxagg
import geosoft.gxpy.grid as gxgrd
import geosoft.gxpy.viewer as gxviewer
gxc = gx.GXpy()
grid_file = 'Wittichica Creek Residual Total Field.grd'
# create a 3D view
with gxview.View_3d.new("TMI in relief",
area_2d=gxgrd.Grid.open(grid_file).extent_2d(),
coordinate_system=gxgrd.Grid.open(grid_file).coordinate_system,
overwrite=True) as v:
v3d_name = v.file_name
# use the data grid as the relief surface
v.set_plane_relief_surface(grid_file)
# add the grid image to the view, with shading, 20 nT contour interval to match default contour lines
gxgroup.Aggregate_group.new(v, gxagg.Aggregate_image.new(grid_file, shade=True, contour=20))
gxgroup.contour(v, 'TMI_contour', grid_file)
# display the map in a Geosoft viewer
gxviewer.view_document(v3d_name, wait_for_close=False)
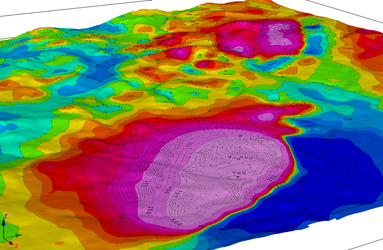
Display Data on the Digital Elevation Model
tmi_on_3d_dem.py
# use the DEM as the relief surface
v.set_plane_relief_surface('Wittichica DEM.grd')
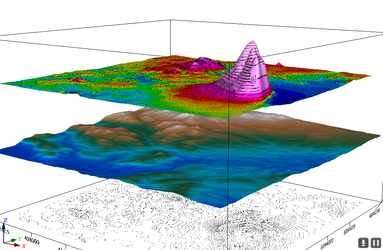
Stacked Planes
A common presentation shows different data layers appearing to float relative to each other. Here we create two floating planes shown relative to the DEM, which is shown as a relief surface at the expected Z elevation. The TMI data is shown as a relief surface floating above the DEM with relief determined by the TMI values, and a contour of the DEM data on a flat plane beneath the DEM surface.
tmi_3d_stack.py
tmi_file = 'Wittichica Creek Residual Total Field.grd'
dem_file = 'Wittichica DEM.grd'
# create a 3D view
with gxview.View_3d.new("TMI drapped on DEM",
area_2d=gxgrd.Grid.open(tmi_file).extent_2d(),
coordinate_system=gxgrd.Grid.open(tmi_file).coordinate_system,
scale=5000,
overwrite=True) as v:
v3d_name = v.file_name
# use the DEM as the relief surface
v.set_plane_relief_surface(dem_file)
gxgroup.Aggregate_group.new(v, gxagg.Aggregate_image.new(dem_file,
color_map='elevation.tbl'))
# relief plane for the TMI, offset to elevation 2000
v.new_drawing_plane('TMI relief')
v.set_plane_relief_surface(tmi_file, base=-4000)
gxgroup.Aggregate_group.new(v, gxagg.Aggregate_image.new(tmi_file))
gxgroup.contour(v, 'TMI_contour', tmi_file)
# add DEM contours on a plane floating beneath the DEM
v.new_drawing_plane('Scratch plane', offset=(0, 0, -2000))
gxgroup.contour(v, 'DEM contour', tmi_file)
# display the map in a Geosoft viewer
gxviewer.view_document(v3d_name, wait_for_close=False)
, multiple selections available,
Related content
Working with Geosoft Maps
Working with Geosoft Maps
More like this
Working with Geosoft Maps
Working with Geosoft Maps
More like this
Python Tutorial for Geosoft GX Developer
Python Tutorial for Geosoft GX Developer
More like this
Python Tutorial for Geosoft GX Developer
Python Tutorial for Geosoft GX Developer
More like this
Python Tutorial for Geosoft GX Developer
Python Tutorial for Geosoft GX Developer
Read with this
Release Notes
Release Notes
More like this